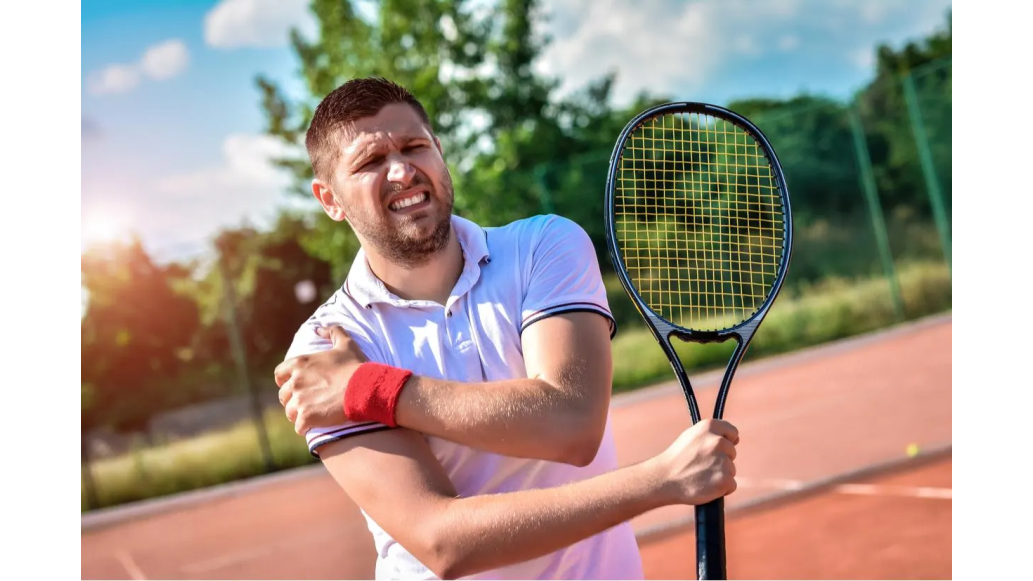
Every shot you make in tennis uses the shoulder, meaning. A shoulder injury can take an athlete off the court at any time. Luckily, there are exercises that can help your athletes recover during rehabilitation and prevent injuries in the future.
Key Takeaways
- THERABAND® resistance training products are a great way to start rehab for an injured shoulder.
- Weak rotator cuff muscles increases the risk of sustaining a shoulder injury.
- Perform shoulder injury rehab with your tennis athletes as part of their strength training routine.
Top Products in This Article
Table of Contents
Shoulder Training Videos for Tennis Players
Reduce the Risk of Shoulder Injury
Tennis Shoulder Injury Rehab Using Elastic Resistance
Shoulder Training Videos for Tennis Players
These exercises can help tennis players strengthen or rehabilitate their shoulder. Ensure your athletes are performing at their best with these exercises!
Tip: Don’t have athletes perform these exercises right before playing tennis. It’s best to do these exercises as part of their strength training routine outside of a tennis match, so you they don’t fatigue their shoulder.
Shoulder Training Program for Tennis Players (Part 1)
This video includes several exercises including some from the Jobe program. The Jobe Four exercises have been studied and shown to highly activate the rotator cuff and scapular (shoulder) muscles.
You will need a:
- Small towel
- THERABAND Soft Weight
- THERABAND CLX® Resistance Band
Part One Exercises:
- THERABAND Soft Weight Exercises
- Side-Lying External Rotation
- THERABAND Soft Weight Prone Shoulder Extension
- THERABAND Soft Weight Prone Horizontal Abduction
- THERABAND Soft Weight Prone Horizontal Abduction
- THERABAND CLX Exercises
- THERABAND CLX External Rotation with Retraction
- Bilateral Shoulder Extension
- External Rotation at 90°
- External Rotation at Side
Shoulder Training Program for Tennis Players (Part 2)
Ready to continue? This next set of exercises will also help with shoulder rehabilitation and conditioning.
You will need a:
- Small towel
- THERABAND CLX Resistance Band
- THERABAND FlexBar®
- THERABAND Soft Weight
- THERABAND Stability Trainer
- Optional exercise mat
Part Two Exercises:
- THERABAND CLX Exercises
- External Rotation with Scapular Retraction
- External Rotation with Oscillation with a THERABAND Flexbar
- 90°/90° Sustained Hold External Rotation
- THERABAND Soft Weight Exercises
- Side-Lying Plyo Drops
- Side-Lying Plyo Catches with a Partner
- Prone 90°/90° Plyo Drops
- 90°/90° Reverse Catch Plyometrics with a THERABAND Stability Trainer and a Partner
- Bonus THERABAND CLX Exercise
- Serratus Plank (with optional mat)
Reduce the Risk of Shoulder Injury
Tennis serves and shots are hard on the shoulder. The motion’s acceleration places stress on the shoulder joint. Then, the four rotator cuff muscles need to act as the “brakes” to stop the arm’s forward motion.

Unfortunately, many tennis players have weak rotator cuff muscles, which can lead to shoulder injuries. These tiny muscles can be tough to target, but elastic resistance bands or tubing is a simple solution.
Tennis Shoulder Injury Rehab Using Elastic Resistance
Wondering why we recommend using resistance bands? They’re the perfect all-in-one solution for your training needs. The slim bands are foldable and portable for use on and off the court.
Compared to traditional weights, resistance bands win in terms of convenience and price, plus they provide the same level of performance. Add a soft weight as the perfect pair for all of your athletes’ tennis exercise needs.
Recap
Follow the exercise videos above to keep your athletes at the top of their game! Strengthening the rotator cuff muscles using these exercises can significantly decrease the risk of your athletes sustaining a shoulder injury during competition.
References
Reynolds, G. (2010). Phys Ed: How to Fix a Bad Tennis Shoulder. The New York Times. Retrieved from https://nyti.ms/2x2FqGl
Medical Disclaimer: The information provided on this site, including text, graphics, images and other material are for informational purposes only and are not intended to substitute for professional medical advice, diagnosis or treatment. Always seek the advice of your physician or other healthcare professional with any questions or concerns you may have regarding your condition.







 US
US France
France Australia
Australia







